Load balancing of OpenShift HA Routers Mind the GARP
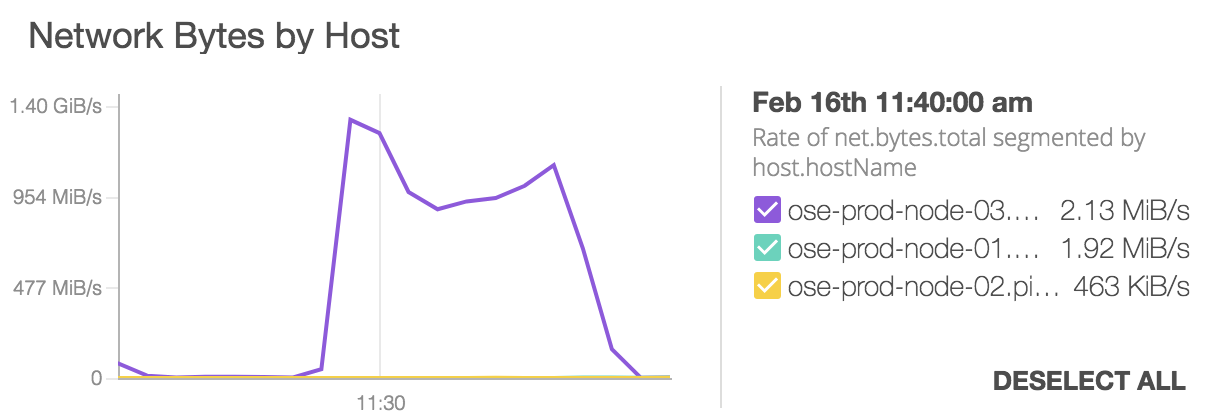
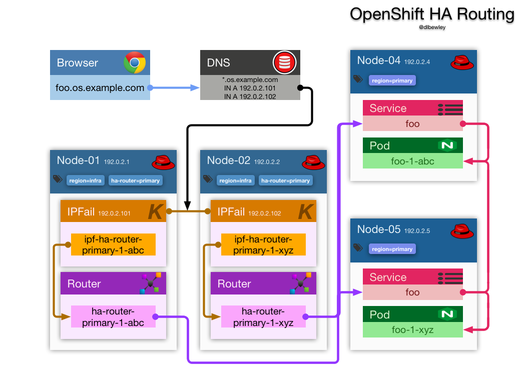
OpenShift HA Routing uses haproxy application routers to get traffic into the cluster. These application routers are made redundant by running ipfailover (keepalived) pods to maintain a set of Virtual IPs on each infrastructure node where the application routers run. These VIPs are then referenced by round robin DNS records to enable a measure of load balancing. OK, so now you are load balancing at the network layer, but what about the link layer?