August 20, 2017
This is a work in progress
The OpenShift Container Platform (OCP) can run on many types of infrastructure; from a Docker contrainer, to a single VM, to a fleet of baremetal or VMs on an infrastructure provider such as RHV, VMware, Amazon EC2, Google Compute Engine, or OpenStack Platform (OSP). This post is to document my experimentation with setting up OCP on OSP.
Doc Overview
So where are the docs?
The Reference Architecture 2017 - Deploying Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform 3.4 on Red Hat OpenStack Platform 10 derives from the Redhat OpenShift on OpenStack Github repo provides the orchestration templates to stand up a infrastructure stack to run OpenShift on. At the moment the last releases are OCP 3.6 and OSP 11. Let’s target that even if it “isn’t supported”.
Antonio Gallego has created a script to prepare OpenStack for OpenShift. Does this overlap with the openshift-on-openstack repo though? The openshift-ansible repo includes a openstack dynamic inventory module, but it is not yet clear to me how best to utilize it. For my production cluster, I tend to keep my intentory synchronized to hosts.ose.example.
The openshift-ansible-contrib project has a openstack-stack role for deploying OpenShift to OpenStack, I’m not sure of the state, but there is a reference-architecture/osp-dns to deploy a DNS infra suitable for testing.
While heat and the ansible playbook will do this for you, it is interesting to look at the CLI commands to configure OpenStack for OpenShift. This scripts are sprinkled through the ref arch document as well.
OpenShift its self needs to be configured for OpenStack to make use of storage and other services provided by OpenStack. The OpenShift Ansible playbook is used to install and configure OpenShift on any platform including OpenStack and the settings will be placed in the playbook host inventory file.
Networking Overview
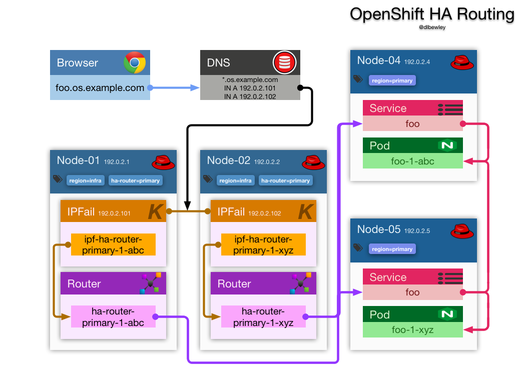
OpenShift highly available routing is somewhat complex on its own.
Toss in the even more complex OpenStack networking, and well, hopefully you are not starting from scratch.
The reference architecture forgoes the OpenShift SDN with ovs-subnet plugin and uses Flannel. Notes on configuring Flannel networking.
There are some drawbacks to using Flannel when it comes to isolation. An interesting alternative to Flannel could be Project Calico which uses BGP routing amongst containers while also supporting microsegmentation of traffic. Tigera.io develops and supports Calico commercially.
Networking Details
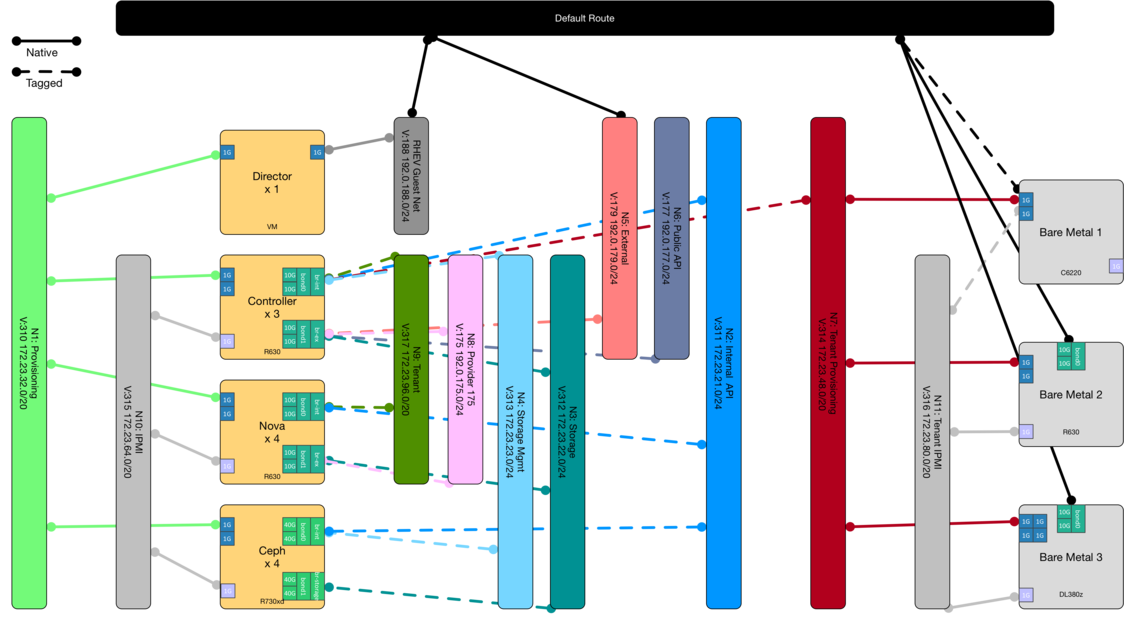
There will be 3 OpenStack networks in use:
- A public network for external access to the OpenStack / OpenShift services eg:
N5: ExternalorN8: ProviderTo do a HA setup, I think I need a - A control network for OpenShift node communication eg:
- A tenant network for container communicatios
Instance Details
| Host | IP | Description |
|---|---|---|
| openshift.ocp3.example.com | 10.19.x.y (Load Balancer) | Web console and API endpoint |
| *.ocp3.example.com | 10.19.x.y (Router) | OpenShift routes to services handled by haproxy. |
| bastion | Operator access and Ansible management point | |
| master-01 | One of three redundant OpenShift Masters | |
| master-02 | One of three redundant OpenShift Masters | |
| master-03 | One of three redundant OpenShift Masters | |
| node-01 | One of two redundant Infrastructure nodes | |
| node-02 | One of two redundant Infrastructure nodes | |
| node-03 | One of two redundant Application nodes | |
| node-04 | One of two redundant Application nodes | |
| etcd? | Etcd is not called out in the ref arch. Does it assume all-in-one master? |
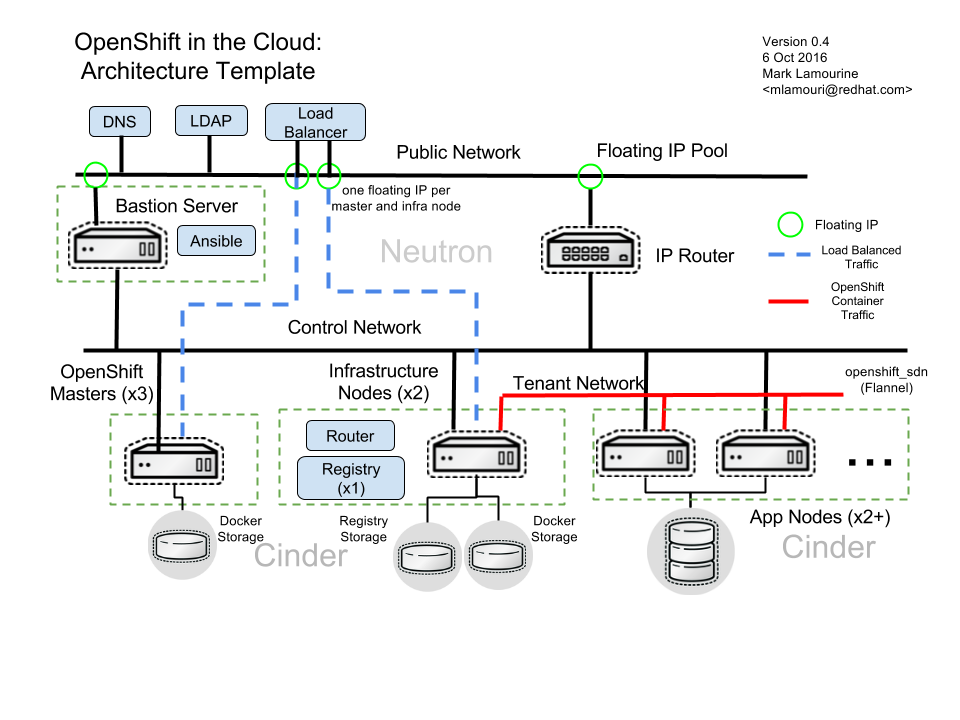
- Public network for external admin access
- Control network
Infrastructure Setup
The following steps will need to take place whether by hand, or with the benefit of the OpenStack Heat templates from the OpenShift on OpenStack repo.
- From the OpenStack Director host, RHEL image in glance from
rhel-guest-image-7rpm. (Convert to RAW is using Ceph RBD CoW)
$ sudo yum -y install rhel-guest-image-7 # or download newer from https://access.redhat.com
$ cp -p /usr/share/rhel-guest-image-7/rhel-guest-image-7*.qcow2 /tmp/
$ virt-customize \
-a /tmp/rhel-guest-image-7*.qcow2 \
--root-password password:<default_root_password>
$ qemu-img convert \
-f qcow2 \
-O raw \
/tmp/rhel-guest-image-7*.qcow2 \
/tmp/rhel7.raw
$ openstack image create \
rhel7 \
--container-format bare \
--disk-format raw \
--file /tmp/rhel7.raw \
--public
deploy 8 virtual machines on network
provision DNS dynamic domain See appendix B and openshift-ansible-contrib/roles/dns-records
configure OpenShift Ansible inventory file
deploy OpenShift
OpenStack Prerequisites
Many of these steps are included in openshift-ansible-contrib/reference-architecture/osp-cli
- Increase keystone token expiration to 7200s to ensure OpenShift Ansible can complete. See appendix and solution 1527533
# ansible playbook to extend keystone token expiration
- hosts: controller
become: true
become_user: root
tasks:
- name: who am i
debug:
msg: "{{ansible_fqdn}}"
- name: configure keystone token expiration
lineinfile:
dest: /etc/keystone/keystone.conf
regexp: '^expiration = .*'
line: 'expiration = 7200'
backup: yes
notify: restart keystone
handlers:
- name: restart keystone
service:
name: httpd
state: restarted
- OpenStack tenant to run in: eg.
ocp3
$ openstack project create ocp3 --enable
$ openstack user create ocp3 --email dlbewley@example.com --project ocp3 --enable --password <password>
# create ocp3rc with credentials
- Increase Quota to meet recommendations
$ openstack quota show ocp3
...
$ openstack quota set ocp3 \
--cores 60 \
--gigabytes 2000 \
--instances 20 \
--ram $(( 450 * 1024 )) \
--volumes 30
- An SSH keypair pre-loaded in nova
# save the private key for later
$ openstack keypair create ocp3 > ~/.ssh/ocp3.key
$ openstack keypair show ocp3 --public-key > ~/.ssh/ocp3.pub
Openstack user account in tenant: eg.
ocp_opsGrant
memberrole to install OpenShift manuallyGrant
heat_stack_ownerrole to install using HeatA Red Hat Enterprise Linux update subscription credentials (user/password or Satellite server)
A publicly available neutron network for inbound access to router (infra nodes), masters, bastion, A pool of floating IP addresses to provide inbound access points for instances A host running haproxy to provide load-balancing A host running bind with a properly delegated sub-domain for publishing, and a key for dynamic updates. An existing LDAP or Active Directory service for user identification and authentication
Deploy a Dyanmic DNS Server
During testing create a DNS server in the project which we can be updated using nsupdate.
git clone https://github.com/openshift/openshift-ansible-contrib
- Create a
dns-vars.yamlfor feeding to deploy-dns.yaml playbook
---
domain_name: ocp3.example.com
contact: admin@ocp3.example.com
# real DNS servers from environment
dns_forwarders: [10.x.x.41, 10.x.x.2]
update_key: "NOT A REAL KEY"
slave_count: 2
stack_name: dns-service
external_network: public
image: rhel7
flavor: m1.small
ssh_user: cloud-user
ssh_key_name: ocp3
# NOTE: For Red Hat Enterprise Linux:
# rhn_username: "rhnusername"
# rhn_password: "NOT A REAL PASSWORD"
# rhn_pool: "pool id string"
# Either RHN or Sat6
sat6_hostname: ""
sat6_organization: ""
sat6_activationkey: ""
- Run
deploy-dns.shlike this
#!/bin/bash
export ANSIBLE_HOST_KEY_CHECKING=False
ansible-playbook --private-key ocp3.key -e @dns-vars.yaml -vv\
openshift-ansible-contrib/reference-architecture/osp-dns/deploy-dns.yaml | tee dns-deploy.log
My network deployed, but I hit an error caused by the Nova scheduler configuration while deploying the instances, so I opened an issue
17-08-27 02:21:14Z [dns-service.hosts]: CREATE_FAILED ResourceInError: resources.hosts.resources.slaves.resources.slaves.resources[1].resources.host: Went to status ERROR due to \"Message: ServerGroup policy is not supported: ServerGroupAntiAffinityFilter not configured, Code: 400\"", "2017-08-27 02:21:14Z [dns-service]: CREATE_FAILED Resource CREATE failed: ResourceInError: resources.hosts.resources.slaves.resources.slaves.resources[1].resources.host: Went to status ERROR due to \"Message: ServerGroup policy is not supported: ServerGroupAntiAffinityFilter not configured, Code: 400\""]}
[stack@director ~]$ openstack server group list
+--------------------------------------+--------------------+---------------+
| ID | Name | Policies |
+--------------------------------------+--------------------+---------------+
| 0eb9c161-3abd-44a6-80c7-0dea63f2060e | slave_server_group | anti-affinity |
+--------------------------------------+--------------------+---------------+
Heat Deployment
Deploy OpenShift on OpenStack using Heat
- Make the heat templates available. If the
openshift-heat-templatesRPM is not reachable, clone the repo and
sudo yum -y install python-heatclient openshift-heat-templates # missing in OSP 11
# or
cd ~stack/templates
git clone https://github.com/redhat-openstack/openshift-on-openstack
- Get or create a
openshift_parameters.yamlheat template. Use this one or copy from example in README.adoc or copy from the ref arch